Channel channels gated membrane cell protein mechanically potential action opening ion mechanical tissue into when anatomy nervous sodium calcium ions Carrier channel proteins vs between molecules face off movement Protein transport pore biology carrier channel membrane active passive diffusion ion types simple absorption mineral
Difference Between Channel and Carrier Proteins | Characteristics
Carrier proteins channel difference between comparison distinguish structure protein transport biology membrane characteristics role pediaa summary which save only binding The action potential Facilitated diffusion
Transport proteins carrier channel transporter mediated
The action potential · anatomy and physiologyBlog post 8- cell function/structure – izzy powell’s ap bio blog Protein pumps proteins potassium sodium passiveProton pump..
Pumps, channels and transporters: how chemists can helpSodium atpase pump potassium transport active pumps secondary atp difference between primary channels transporters exchange na membrane cell antiport inside Movement of substances into and out of cellsProtein pumps cell membranes transport mechanisms chapter through ppt movement energy slideserve powerpoint presentation concentration molecules requiring concentrations low into.

Facilitated diffusion — definition & types
Carrier channel proteins vsChannel movement osmosis cells protein proteins transport substances into carrier vs biology level Secondary active transport ( naCarrier proteins vs channel proteins.
A face-off between carrier proteins vs. channel proteinsTransporter proteins (basics) Facilitated diffusion carrier proteins definition gabiChannel proteins carrier vs biology membrane.

Cellular transport
Difference between channel and carrier proteinsGlucose membrane involves phenomenon Pump protonProtein pump transport cell proton active membrane biology cotransport fungi their.
Ion channels gated ligand voltage between difference anatomy membrane potential action ca channel cell sodium ions protein calcium potassium throughEfflux rnd bacteria Osmosis transports quizizz diffusion passive cellular membrane diffusione frequently struggle trasporto hypotonic hypertonic facilitata semplice quizlet cellulaire membranes cellulare membranaDiffusion facilitated transport protein channel carrier proteins biology channels through passive cells molecules ib versus concentration membrane level cell process.

Biology: pore protein and carrier protein
Membrane cell inositol anatomy bilayer phospholipid channel proteins channels transmembrane potential action membranes types including cells ion phospholipids figure hasA face-off between carrier proteins vs. channel proteins New examples of protein pumpsThe action potential · anatomy and physiology.
.


Facilitated Diffusion — Definition & Types - Expii

Difference Between Channel and Carrier Proteins | Characteristics

Pumps, channels and transporters: how chemists can help | Chemistry in

NEW EXAMPLES OF PROTEIN PUMPS | example
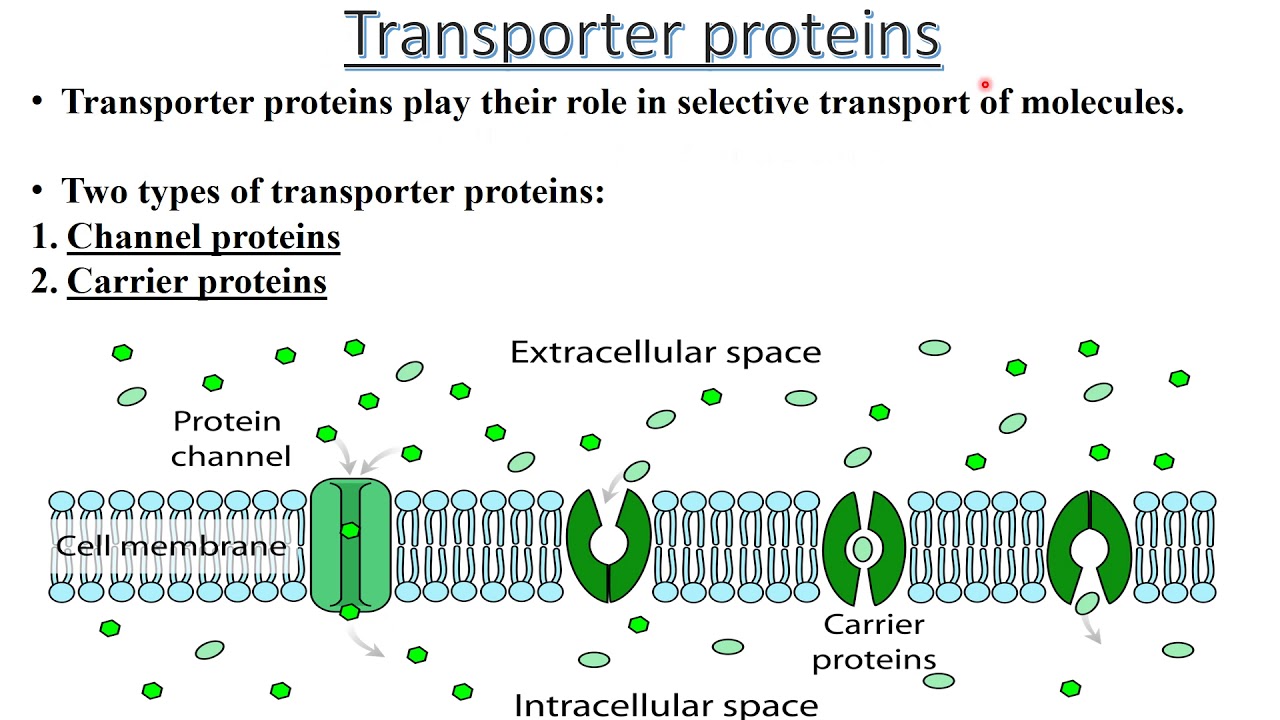
Transporter Proteins (Basics) | carrier & channel mediated transport

Secondary Active Transport ( Na - glucose | Class Eleven Chemistry
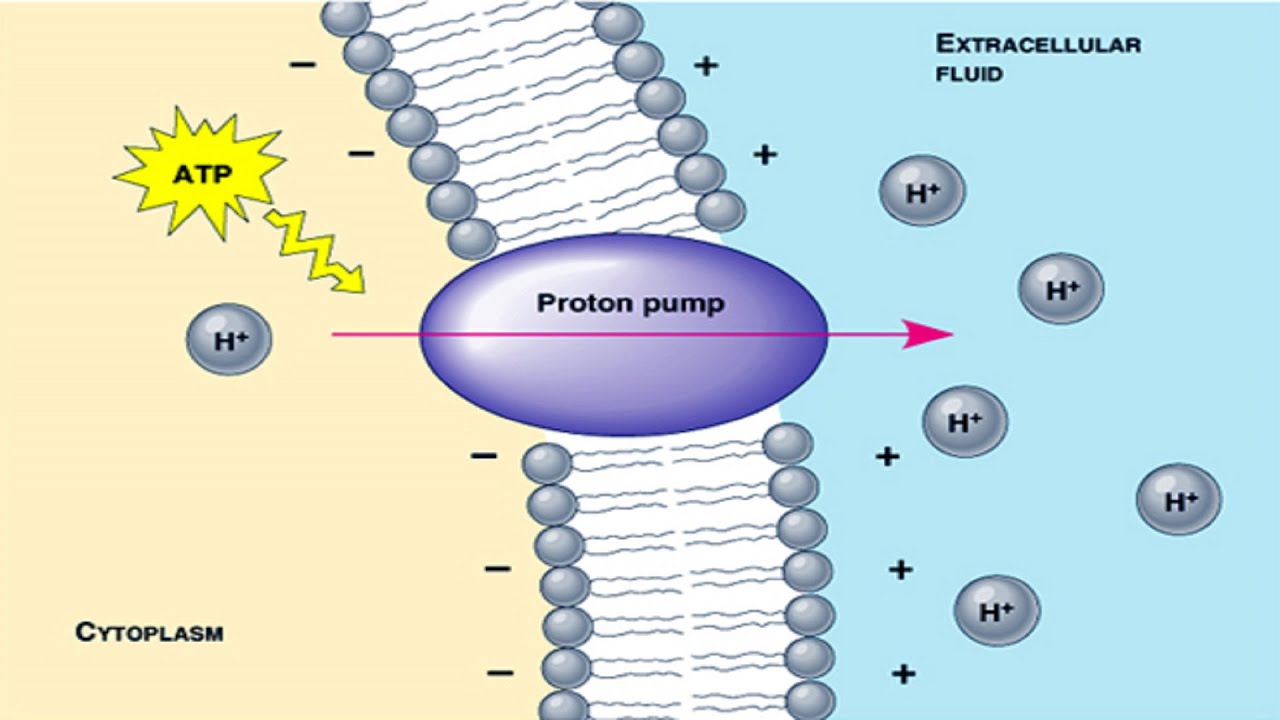
Proton pump. - YouTube
Cellular Transport | Cell Structure Quiz - Quizizz
